cocos2d-html5(以下简称ch5)是一款用javascript和html5实现的,基于cocos2d-x的游戏引擎,相对于另外一款以javascript编写的游戏引擎,
cocos2d-js,ch5具有体积小,结构简单的优点,特别适合各种Web小游戏的开发,尤其是当下很火爆的微信社交小游戏,我将以一款简单的拼图游戏为例子,介绍一下如何从零开始快速使用ch5开发游戏。
首先看一下目录结构:
这里的app.js是我们的主要js文件,WeixinApi.js是微信的官方APIJS,如果要接入微信的朋友圈分享功能需要用到这个文件,index.html文件是主要
的展示文件,其作用只是提供一个canvas标签以及引入需要的js文件,res目录则是存放游戏用到的各种图片资源。cocos2d-js-v3.1-lite.js则是cocos2d-html5的库文件,我们需要用到的所有api都被压缩到了这个js文件里面,体积小,便于快速加载。目录大概就是这么多,我们需要编写的逻辑都在app.js里面了,当然这个文件你也可以自己命名,只要在html文件中引入就行。
介绍完了目录结构,我们再看看对于一个游戏开发的小白来说,开发一个简单的ch5游戏,我们需要知道哪些知识。
1、Scenes 场景
就是指游戏运行的背景和总体环境,可以是一张简单的背景图片,也可以是多个图片叠加形成的复杂图形。一个游戏可以有多个不同的场景,但是在游戏运行的某一个特定时刻,场景是不变的。
2、Director 导演
导演是指游戏中负责变换和初始化产后场景的元素,相当于整个游戏中的舞台设计师。
3、Layers 层
层的概念可以理解为场景的组成元素,他是精灵的直接载体,多个层的叠加就可以组成我们需要的游戏效果。
4、sprites 精灵
精灵是整个游戏中的基本单元,同时是一个资源对象,可以进行各种动画动作,如旋转、移动、放大等等,我们看到的游戏效果,大部分都是通过精灵来实现的。
以上就是整个ch5游戏中主要的元素,一个完整的游戏应该包括以上每个元素。
游戏的截图如下:
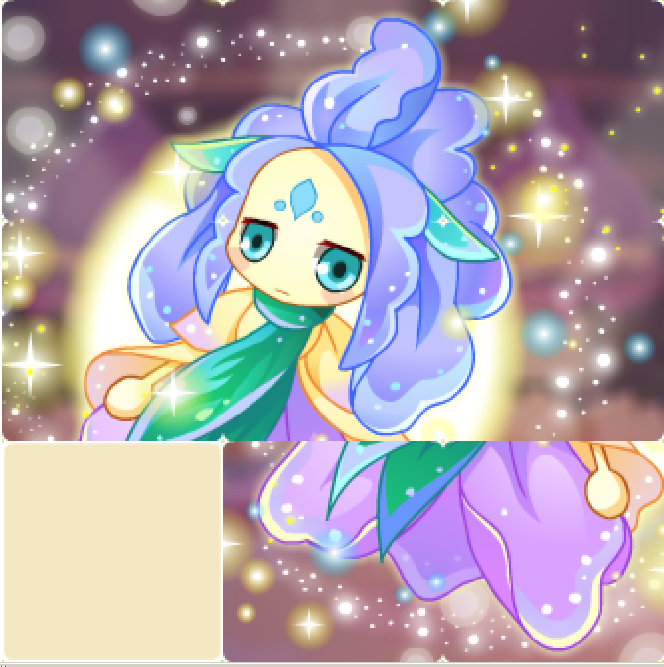
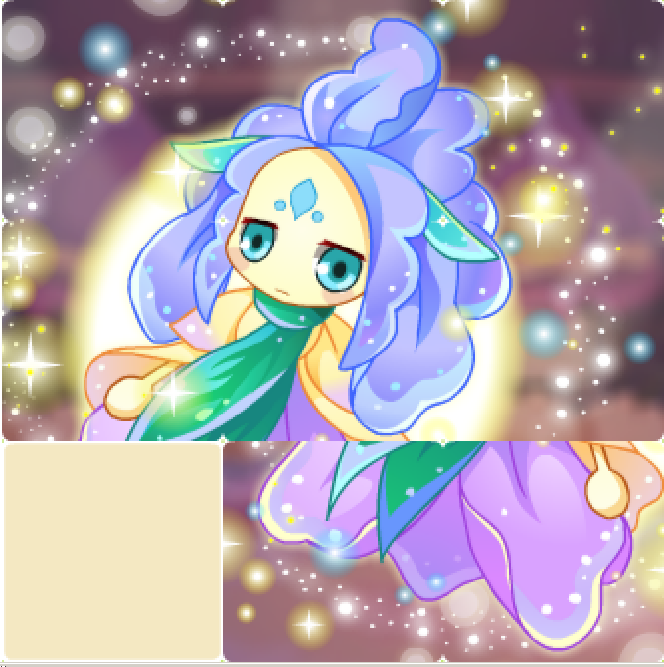


游戏资源文件共有10个,一个背景图片组成一个场景,9个小图片就是精灵,而9个小图片又一起组成一个层,叠加在背景层之上,通过导演来调用9个精灵元素的相互交换和移动,完成游戏。
具体的代码分析如下:
var PieceSprite = cc.Sprite.extend({
id:0,
_touchBegan: false,
_touchEnabled: true,
beginX:0,
beginY:0,
ctor: function (image,id) {
this._super();
this.init(image);
this.id=id;
},
onEnter: function () {
//cc.Director.getInstance().getTouchDispatcher()._addTargetedDelegate(this, 0);
this._super();
cc.eventManager.addListener({
event: cc.EventListener.TOUCH_ONE_BY_ONE,
swallowTouches: true,
onTouchBegan: this.onTouchBegan,
//onTouchMoved: this.onTouchMoved,
onTouchEnded: this.onTouchEnded
//onTouchCancelled: this.onTouchCancelled
}, this);
},
onExit: function () {
//cc.Director.getInstance().getTouchDispatcher()._removeDelegate(this);
//当Sprite退出后,取消点击事件的注册。
this._touchEnabled = false;
this._super();
},
onTouchBegan: function (touch, event) {
//console.log(touch.getLocation());
//console.log(this);
if (cc.rectContainsPoint(this._node._getBoundingBoxToCurrentNode(), touch.getLocation())) {
//当点击在 Sprite 范围内时,执行。
//在这里处理点击事件。
this._touchBegan = true;
//this.beginX= touch._prevPoint.x;
//this.beginY= touch._prevPoint.y;
this.beginX= touch.getLocation().x;
this.beginY= touch.getLocation().y;
return true; //返回true, 才会执行 onTouchEnded方法。
}
return false;
},
onTouchEnded: function (touch, event) {
if (touch._point.x - this.beginX > 20) {
//this.rightCombineNumber();
//console.log("right");
//alert("right");
doAction("right",this._node.id);
}
else if (touch._point.x - this.beginX < -20) {
//this.leftCombineNumber();
//console.log("left");
//alert("left");
doAction("left",this._node.id);
}
else if (touch._point.y - this.beginY > 20) {
//this.upCombineNumber();
//console.log("up");
//alert("up");
doAction("up",this._node.id);
}
else if (touch._point.y - this.beginY < -20) {
//console.log("down");
//alert("down");
doAction("down",this._node.id);
}
else{
alert(this.beginX);
//alert(touch._point.x);
alert(touch.getLocation().x);
alert(this.beginY);
//alert(touch._point.y);
alert(touch.getLocation().y);
}
if (this._touchBegan) {
this._touchBegan = false;
}
}
});
以上是精灵类的封装,主要定义了具体的动作。
var MyScene = cc.Scene.extend({
cat:null,
touchbeginpos:null,
onEnter:function () {
this._super();
var size = cc.director.getWinSize();
//Manager.init(this);
var scoreLabel = new cc.LabelTTF("0", "黑体", 24, cc.size(150, 30), cc.TEXT_ALIGNMENT_LEFT);
this.addChild(scoreLabel);
scoreLabel.attr({
x:30,
y:cc.director.getVisibleSize().height - 25,
strokeStyle: cc.color(0,0,0),
lineWidth: 2,
color: cc.color(255,150,100),
anchorX:0.1
});
var BgLayer = new BackgroundLayer();
this.addChild(BgLayer);
var playLayer = new PlayLayer();
this.addChild(playLayer);
cc.eventManager.addListener({
event:cc.EventListener.TOUCH_ONE_BY_ONE,
swallowTouches:true,
onTouchMoved:function(touch, event){
},
onTouchEnded:function(touch, event)
{
},
onTouchBegan:function(touch, event)
{
return true;
}
},this);
if(mTimeLayer==null){
mTimeLayer = new TimeLayer();
}
mTimeLayer.setLabel(60);
this.addChild(mTimeLayer);
if(mTimeLayer.isRunning==false){
mTimeLayer.run();
}
}
});
这个是场景的初始化,通过多个层进行叠加。
//背景图
var BackgroundLayer = cc.Layer.extend({
ctor:function () {
this._super();
this.init();
},
init:function () {
this._super();
var winsize = cc.director.getWinSize();
//create the background image and position it at the center of screen
var centerPos = cc.p(winsize.width / 2, winsize.height / 2);
var spriteBG = new cc.Sprite("res/bg.png");
//console.log(spriteBG);
spriteBG.setPosition(centerPos);
this.addChild(spriteBG);
}
});
这个是一个简单的背景层。
以上就是ch5游戏开发中的主要几个类和函数,基于这些,我们可以开发一些简答的小游戏。
ps:
关于如何初始化拼图游戏中的图片位置的问题,即如何摆放各个小图片的位置,从而保证拼图是可以有解的?对于简单的拼图游戏来说,我们可以先将场景排成正确的位置,然后将空白块和周围相邻的其他方块进行多次的随机交换,这个过程本身就是模仿玩家的移动,所以,它肯定是可逆的,因此总是能保证有解。
git地址:
https://github.com/wengang285/puzzle



